If you don’t, then don’t worry – just have a quick read of our sister article and then come back here. To figure this out, as with most things, when you’re working with different timeframes, it’s a good idea to work with the timeline. The value of a company, or a stock, a business, etc, is all fundamentally based on the Present Value of future expectations.
How are future value and present value related?
In a nutshell, then, we can say that the Present Value is nothing but the sum of the discounted future cash flows. And take your time to see how we’re discounting future cash flows to get to the present value. A mentioned, the discount rate is the rate of return you use in the present value calculation. It represents your forgone rate of return if you chose to accept an amount in the future vs. the same amount today.
Present Value of Multiple Cash flows
So, if you’re wondering how much your future earnings are worth today, keep reading to find out how to calculate present value. Present value is important because it allows investors and businesses to judge whether some future outcome will be worth making the investment today. It is also important in choosing among potential investments, especially if they are expected to pay off at different times in the future.
How to use present value for investing?
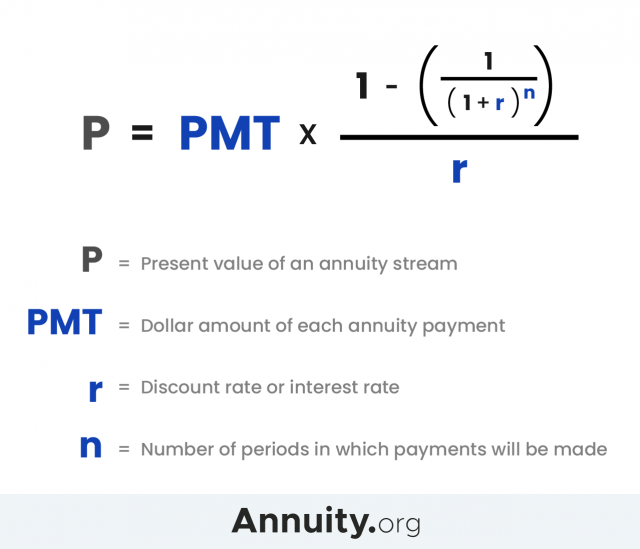
Assuming that the discount rate is 5.0% – the expected rate of return on comparable investments – the $10,000 in five years would be worth $7,835 today. The Present Value (PV) is a measure of how much a future cash flow, or stream of cash flows, is worth as of the current date. When the discount rate is annual (i.e. as with an interest rate on a certificate of deposit), and the period is a year, this is equivalent to the present value of annuity formula.
We can use a formula to help us determine a future value when the calculations get more complex with more years. Let’s start with a formula that helps us determine the value of an amount of money at a future date, or the future value formula. Compound interest is like the secret power of a superhero because it gives you powerful growth of your savings over time. Compound interest is when you earn interest every year not only on the original amount you deposit into an account, but you also earn interest on interest! Let’s look at an example to see how compound interest and different interest rates, the percentage at which money grows over a specified period, impact the growth of your money over time.
- In the case of not having a consistent rate, it wouldn’t be so easy to calculate the present value.
- Money is worth more now than it is later due to the fact that it can be invested to earn a return.
- For a brief, educational introduction to finance and the time value of money, please visit our Finance Calculator.
As shown in the future value case, the general formula is useful for solving other variations as long as we know two of the three variables. This is because at 12% the $15,000 is actually worth $8,511.45 today, but you would need to make an outlay of only $8,000. According to these results, the amount of $8,000, which will be received after 5 years, has a present value of $4,540. However, if your $1 is worth $0.90 tomorrow, your PV will be less than 1. Present value is used as a starting point for assessing the fairness of a future financial liability or benefit.
Due to the relationship between future and present values, the present value table is the inverse of the future value table. In present value situations, the interest rate is often called the discount rate. Some individuals refer to present value problems as “discounted present value problems.” The amount you would be willing to accept depends on the interest rate or the rate of return you receive. For example, suppose you want to know the value today of receiving $15,000 at the end of 5 years if a rate of return of 12% is earned.

Present value uses the time value of money to discount future amounts of money or cash flows to what they are worth today. This is because money today tends to have greater purchasing power than the same amount of money in the future. Taking the difference between operating versus financial capital lease same logic in the other direction, future value (FV) takes the value of money today and projects what its buying power would be at some point in the future. Present value (PV) is the current value of an expected future stream of cash flow.
Keep reading to find out how to work out the present value and what’s the equation for it. For example, $1,000 today should be worth more than $1,000 five years from now because today’s $1,000 can be invested for those five years and earn a return. If, let’s say, the $1,000 earns 5% a year, compounded annually, it will be worth about $1,276 in five years. Present value is based on the concept that a particular sum of money today is likely to be worth more than the same amount in the future, also known as the time value of money. Conversely, a particular sum to be received in the future will not be worth as much as that same sum today. Calculate the present value of this sum if the current market interest rate is 12% and the interest is compounded annually.
You expect to earn $10,000; $15,000; and $18,000 in 1, 2, and 3 years’ times respectively. What if your parents offered to give you the value of what $1,000 to be received in the future is worth today instead of having to wait one year? The value of the $1,000 today is called the discounted value (or present value) and is simply the future value minus the interest you would receive over the next year.
Input the future value of the amount you expect to receive in the numerator of the formula. As always, because we’re working with timeframes over here, it’s a good idea to start with the timeline. And because this particular cash flow represents the cash in the present, we can essentially see this as the present value.

